James Gregory and His Contributions To Telescopes
James Gregory was a Scottish mathematician and astronomer, born in November 1638 in Drumoak, near Aberdeen, Scotland. He is best known for his description of the first practical reflecting telescope, now known as the Gregorian telescope. James Gregory made important mathematical discoveries, including infinite series representations for various trigonometric functions. Despite his significant contributions to the fields of mathematics and astronomy, there is no mention of any notable awards or honors received by Gregory.
Who is James Gregory astronomer?
James Gregory was a Scottish mathematician and astronomer, born in November 1638 in Drumoak, near Aberdeen, Scotland. He was educated at Marischal College (later part of the University of Aberdeen), where he graduated in 1657. Gregory is best known for his description of the first practical reflecting telescope, now known as the Gregorian telescope. He also made significant advancements in trigonometry and calculus, including discovering infinite series representations for several trigonometric functions and contributing to the fundamental theorem of calculus.
James Gregory is known for his contributions to the field of telescope design, particularly the invention of the Gregorian telescope and the development of the reflecting telescope.

Fig 1: James Gregory
What is Gregorian telescope?
The Gregorian telescope is a type of reflecting telescope that was first published by Scottish mathematician James Gregory in 1663. It is known for its unique optical design, which utilizes a concave secondary mirror to reflect and focus light. According to the Gregorian design, the primary mirror must have a hole at the center, and the secondary mirror is positioned beyond the focal point of the primary mirror, making the telescope larger. The image is focused before the secondary mirror, allowing for a stop to be placed in the tube to block extra light and restrict heat transmission, which is particularly useful in solar observations. The Gregorian design is also known for not causing optical problems like chromatic and spherical aberration. This design is used in many modern telescopes, including the Vatican Advanced Technology Telescope, the Magellan telescopes, and the Large Binocular Telescope. The Giant Magellan Telescope will also use Gregorian optics. The size of the telescope’s aperture directly impacts its ability to gather light and resolve fine details, with larger apertures offering greater performance.
The Gregorian Telescope is basically a reflector telescope invented and designed by well known 17th century mathematician and astronomer James Gregory (1638-1675). He was born in Scotland and was a contemporary of Sir Isaac Newton. Both the scientists worked together on different projects. However, Gregory had proposed the design of his reflector telescope in 1663 in a publication called ‘Optica Promota’ before Newton built his first reflector telescope in 1668. But Gregory did not build his telescope practically; it was just a hypothesis then. Finally, in 1673, after 5 years of the building of Newton’s Telescope, this Gregorian Telescope got its physical appearance. However, it was the first practical telescope design in history and as a credit, the design of the scope is named after the inventor, James Gregory.

Fig 2: Gregorian Telescope
After publishing his theoretical design, Gregory tried multiple times to build it. As he did not have practical skills and did not find any optician to help him, he ultimately failed to build one. Later, Robert Hooke, an experimental scientist showed his interest to work on it and finally successfully built it in 1673. Moreover, Scottish optician James Short made Gregorian Telescope with highly reflective parabolic mirrors.
The Gregorian design was a very successful optical instrument to view the night sky and was widely used at that time due to its high performance for more than a century. Though by time, the design was improved by several scientists later. Nowadays the use of this telescope is rare for some reasons, yet there are some special fields, where it is used still now.
Did James Gregory invent the first reflecting telescope?
James Gregory did not invent the first reflecting telescope, but he did make significant contributions to its design and development. Gregory’s involvement with telescopes began in the early 1660s when he was a professor at the University of St Andrews. During this time, he published a book called Optica Promota, which explored various aspects of optics and included a design for a new type of telescope that used mirrors instead of lenses. This design, now known as the Gregorian telescope, aimed to correct the spherical and chromatic aberration seen in refracting telescopes by using a parabolic mirror and a concave secondary mirror with an elliptical surface.
Gregory’s design for the Gregorian telescope was a notable milestone in the history of telescopes, as it marked the first published proposal for a reflecting telescope. However, he was not able to construct it himself due to his lack of practical skills and inability to find a suitable optician. It was not until ten years later that the design was actually constructed. In 1663, Gregory visited the Royal Society in London and presented his design for the Gregorian telescope. The society commissioned the construction of the telescope, which was ultimately built by the English scientist and mathematician, Robert Hooke, in 1673.
Did James Gregory Create a Design For a Reflecting Telescope?
James Gregory described his reflecting telescope design in his 1663 publication, Optica Promota. This design is now known as the Gregorian telescope. The Gregorian telescope design uses a parabolic primary mirror and a concave secondary mirror with an elliptical surface, which corrects spherical and chromatic aberration. Although Gregory lacked the practical skills to construct the telescope, his design attracted attention from scientists like Robert Hooke, who successfully built the telescope 10 years later. The Gregorian telescope design offers a wider aperture, a deeper field of view, and collects more light, providing a brighter image, which made it popular among amateur astronomers.
What Was James Gregory’s Design for a Reflecting Telescope?
James Gregory’s design for a reflecting telescope used a metal mirror to reflect light rather than a glass lens that refracts the light. The primary mirror was concave, with the precise curve being a parabola, to help focus the image. Gregory’s design included a second, smaller mirror that bounces the light to the eyepiece, a configuration now known as the Cassegrain configuration. The secondary mirror had an elliptical surface, placed past the focal point of the primary mirror, reflecting the image back through a hole in the primary mirror where it could be conveniently viewed. Gregory’s design aimed to correct spherical aberration as well as the chromatic aberration seen in refracting telescopes. The Gregorian telescope, as it came to be known, was compact and portable, offering a wider aperture and a deeper field of view, which allowed it to collect more light and provide a brighter image. Although Gregory described his design in his 1663 Optica Promota, he lacked the practical skills to construct it and had to wait until 1673 when Robert Hooke was able to build the telescope.
The Gregorian design used basically two mirrors. The primary mirror was used as the main light-gathering mirror. The other mirror was the secondary mirror which was located beyond the focal point of the primary mirror. The light reflected from the primary mirror to the secondary mirror and then went out of the telescope along a small hole in the primary mirror.
The pathways of lights passing through the Gregorian telescope
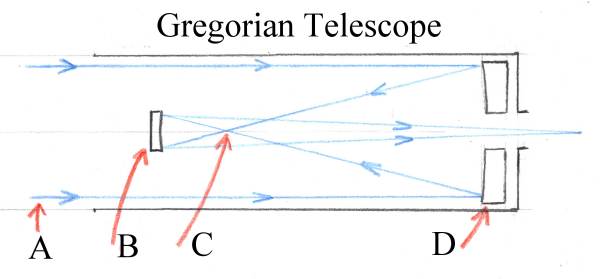
Fig 3: The pathways of lights passing through the Gregorian telescope.
In the figure, we can see that, as light travels through the telescope, it at first enters the tube at A and then reflects by the primary mirror (D). The primary mirror used here is a concave parabloid. So the light is reflected by the primary mirror and the light travels to the secondary mirror (B). This mirror B is a concave ellipsoid and it is located at the focal point (C) of the primary Mirror (D). This arrangement allows the image of the telescope located on the right side up which is advantageous for sky observation. This is an advanced version of Newton’s Telescope as the Newtonian telescope made the inverted images.
Limitations and Disadvantages of Gregorian Telescope
- James Gregory used two concave mirrors in his reflector telescope which is more complicated to make compared to the Newtonian Telescope. Newton used only one concave mirror and a flat mirror.
- According to the Gregorian design, the primary mirror must have a hole at the center. But making a hole in a mirror and exactly at the center is a tough job.
- The Gregorian design makes the telescope larger because the secondary mirror is beyond the focal point of the primary mirror.
Advantages of Gregorian Telescope
- According to the Gregorian design, the image is focused before the secondary mirror, there, we can place a stop in the tube, which will block the extra light from reaching the secondary mirror. This system makes the views of the objects that are seen by the telescope clearer. Besides, this also restricts the heat transmitted. This is very useful in solar observations and experiments. Even now, this design and setup are used in many modern telescopes.
- We know that the refractor telescope has some optical problems like chromatic and spherical aberration. The Gregorian telescopes do not cause these problems.
- The Gregorian design offers a unique upright image which is why still, in some secondary or smaller sighting telescopes, this design is used.
However, nowadays, the Gregorian design is replaced by Cassegrain Telescopes, which provide higher performance, though it has a lot of similarities.
Modern Observatories that use the Gregorian Design
You will find the Gregorian telescopes in Mount Graham International Observatory In Arizona if you look through the Vatican Advanced Technology Telescope and the Large Binocular Telescope. This design is used also in many radio telescopes like Green Bank Telescope which is kept at the NRO in West virginia. In Puerto Rico, the well-known Arecibo Radio Telescope is also a Gregorian telescope.
Modern Day Improvement on the Gregorian
The optical system of the Gregorian design has been advanced a lot nowadays to overcome the limitations. Instead of the previous system, experimental scientists implemented the Compact Gregorian Reflector. This is an advanced optics system that significantly reduces the telescope’s size.

