Eagle Nebula: Definition, Location, Size, Age, Visibility
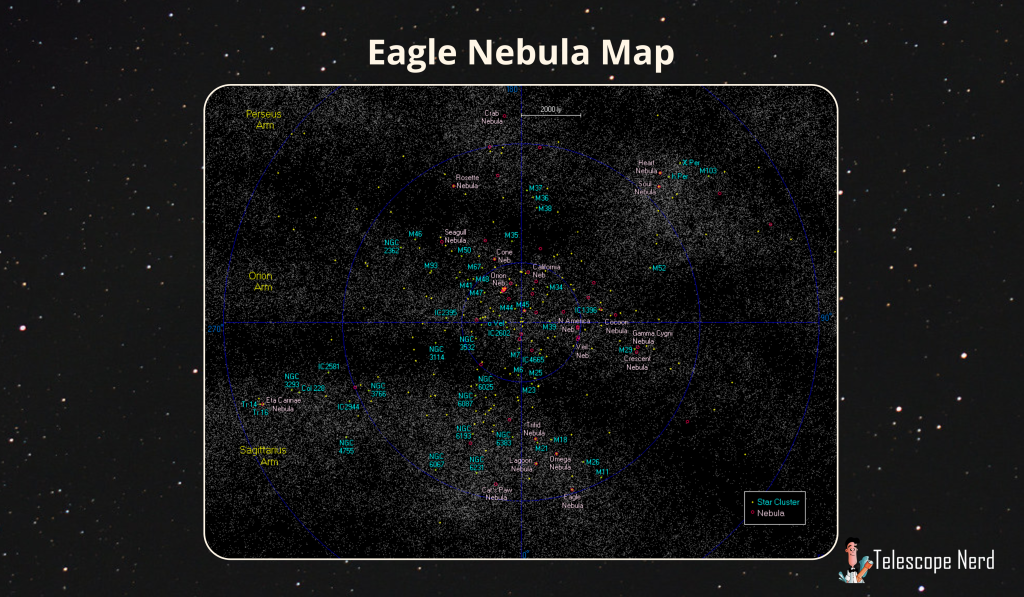
The Eagle Nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust, cataloged as Messier 16. The Eagle Nebula is one of the brightest nebulae in the night sky. The nebula is a bright emission nebula, located in the constellation Serpens Cauda. The Eagle Nebula is located 7,000 light-years from Earth within the Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way galaxy. The Eagle Nebula lies in the Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way.
The Eagle Nebula spans about 55 light-years across. It covers an area of 70 by 55 light-years. The Eagle Nebula is the site of a vast star-forming region. It is visible in both the northern and southern hemispheres. The Eagle Nebula is 5.5 million years old.

What is the Eagle Nebula?
The Eagle Nebula is an area of active star formation, containing active star-forming gas and dust regions. The Eagle Nebula is known as the Star Queen Nebula, and it is home to the Pillars of Creation. The Eagle Nebula spans 70 by 55 light-years and is located about 7,000 light-years from Earth.
The Eagle Nebula is a bright magnitude 6.2 emission nebula. It is catalogued as Messier 16 and NGC 6611. The nebula was discovered in 1745 by the Swiss astronomer Jean-Philippe Loys de Chéseaux. It is recognizable by the eagle-like silhouette of the dark part of the nebula that it is named for. The Eagle Nebula is further towards the center of the Milky Way than we are.
Messier 16 is a nebula 7,000 light-years away. A GAIA study published in the Astrophysical Journal in January 2019 suggests the Eagle Nebula is closer. NGC 6611 is the rich young star cluster embedded in the Eagle Nebula. The region contains gas and dust which are active star-forming materials. Some gas collapsed and formed hot bright O stars.
The Hubble image of the Pillars of Creation was taken in 1995. These structures are part of the active star-forming regions within the nebula. The Eagle Nebula continues to be an area for astronomical study.
What are the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula M16?
The Pillars of Creation are part of the Eagle Nebula depicting elephant-like trunks of interstellar gas and dust within the nebula. These three pillars are the most notable feature of this nebula. Pillars of Creation are part of an active star-forming region within the nebula. The nebula contains several active star-forming gas and dust regions, including the Pillars of Creation. The Pillars of Creation stretch roughly 4 to 5 light-years tall.
Pillars of Creation are made primarily of cool molecular hydrogen and dust. Finger-like structures larger than the solar system protrude from the tops of the pillars. These structures are being eroded by fierce winds and ultraviolet light from nearby hot, young stars. Winds from newborn stars are slowly eroding the towers of gas and dust. The Pillars of Creation hide newborn stars in their wispy columns.
Astronomers and artists modeled the Pillars of Creation using Hubble and Webb space telescopes. The Herschel Space Observatory captured a new image of the Pillars of Creation in far-infrared wavelengths.

Where is the Eagle Nebula located?
The Eagle Nebula is located in the constellation Serpens Cauda. The nebula lies in the Sagittarius Arm of the Milky Way. The Eagle Nebula is located about 7,000 light-years from Earth. This active star-forming region contains gas and dust. It is known for the Pillars of Creation, which are part of the larger emission nebula IC 4703. The nebula spans approximately 55 light years. Astronomers observe this region to understand active star-forming processes.
What is the size of the Eagle Nebula?
The Eagle Nebula spans 70 by 55 light-years, with an angular size of 7 arc-minutes. The Extended wings of the Eagle Nebula spread nearly 120 light-years wide. Eagle Nebula contains 376 stars.
The Eagle Nebula has an apparent magnitude of 6 and an absolute magnitude of -8.21. The distance to the Eagle Nebula is 7,000 light-years. Columns of cold gas and dust are 6,500 light-years distant in the Eagle Nebula. These structures are part of the star-forming regions known as the Pillars of Creation.
How old is the Eagle Nebula?
The Eagle Nebula is estimated to be 5.5 million years old. Some sources suggest the Eagle Nebula age is closer to 6 million years. The star forming region within the nebula contains the cluster NGC 6611. The Eagle Nebula cluster age is estimated at 1–2 million years. This younger age reflects the ongoing processes within the Pillars of Creation. These structures highlight active star formation in the region. The nebula’s age and features make it a key object of study. Scientists focus on understanding its evolution and dynamics. The combination of older and newer components shows its vast history.
Is the Eagle Nebula visible?
The Eagle Nebula is visible from both northern and southern hemispheres. In the northern hemisphere, it is best viewed from June to September. In the southern hemisphere, it remains visible during corresponding months. The star cluster in the Eagle Nebula has an apparent magnitude of 6. This makes it easy to find through a small telescope.
The Pillars of Creation, a well-known feature within the Eagle Nebula, require a minimum 250 mm (9.84 in) aperture telescope to view. These structures, made of gas and dust, are part of the Messier 16 region. They stand 5 light years tall and are a site of active star forming activity. A space telescope provides optimal viewing conditions for such distant objects.
How are the Eagle, Omega, Trifid, and Lagoon Nebulae connected, and how does the Eagle Nebula compare to the Orion Nebula?
The Eagle Nebula, the Omega Nebula, the Trifid Nebula, and the Lagoon Nebula are part of the same spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy. These nebulae are regions of active star formation. They contain large amounts of gas and dust which contribute to the birth of new stars. The Eagle Nebula is similar to the Orion Nebula in terms of structure. Both nebulae host young star clusters. The Orion Nebula is closer to Earth which makes it more visible. The Eagle Nebula is larger in size and contains more intricate structures.

