Dobsonian Telescope: Definition, Mounts, Comparison
A Dobsonian telescope is a type of Newtonian reflector telescope, known for its unique design and functionality. It was popularized by John Dobson in the 1960s with the aim of making telescopes more accessible to the public. The telescope uses a simple altazimuth mount, which allows easy movement in two directions: altitude (up and down) and azimuth (left and right). This simplicity in design makes it user-friendly, even for beginners. The Dobsonian telescope is primarily used for visual observation of celestial objects and is not used for astrophotography due to its manual tracking system.
The Dobsonian mount, a modified version of the altazimuth mount, is used with Dobsonian telescopes. This mount, usually made of wood, provides stable support for Newtonian telescopes. It doesn’t require leveling and is primarily used for visual observations, not astrophotography. Some Dobsonian mounts come with motorized systems for smoother and more accurate tracking of celestial objects.
The difference between a Dobsonian and a Newtonian telescope lies in their mounting systems. A Dobsonian telescope is a type of Newtonian telescope that employs a specific altazimuth mount, known for its simplicity and affordability. Newtonian telescopes, on the other hand, can utilize various mounts, including equatorial mounts. The Dobsonian telescope’s design prioritizes simplicity and portability, making it an ideal choice for beginners or those seeking a straightforward observational experience.
What is a Dobsonian telescope?
A Dobsonian telescope is a type of Newtonian reflector telescope that has revolutionized the way amateur astronomers observe the night sky. The meaning of Dobsonian is rooted in its unique design and functionality. Dobsonian telescope is characterized by its use of a simple altazimuth mount, which allows easy movement in two directions: altitude (up and down) and azimuth (left and right). This straightforward design makes it incredibly user-friendly, even for beginners.
Dobsonian telescope was popularized by John Dobson in the 1960s. Dobson, an American amateur astronomer, sought to make telescopes more accessible to the public. John achieved this by designing a telescope that offered a large aperture at a relatively low cost. The large aperture is a significant advantage as it allows for more light to be gathered, resulting in clearer and more detailed views of celestial objects.
Dobsonian telescopes are primarily used for visual observation of celestial objects. Dobsonians are not used for astrophotography due to their manual tracking system. The telescope tube houses the mirrors, which are the heart of the telescope. This tube is then mounted on a base, allowing for easy movement and adjustment. The simplicity of the design makes it a popular choice among amateur astronomers.
The affordability and ease of use of Dobsonian telescopes have made them a favorite among amateur astronomers. Dobsonians offer a high-quality viewing experience without the high price tag often associated with other types of telescopes. The larger the aperture of a Dobsonian telescope, the better its light-gathering capabilities, resulting in more detailed views of celestial objects. This makes them an excellent choice for those looking to observe deeper into the wonders of the universe.
What sizes of Dobsonian telescopes exist?
Common sizes of Dobsonian telescopes are listed below.
- Tabletop Dobsonian telescopes: 4.5 to 6 inches
- Small Dobsonian telescopes: 6 to 10 inches
- Medium-sized Dobsonian telescopes: 12 and 16 inches
- Large Dobsonian telescopes: 18 to 24 inches
- Extra-large Dobsonian telescopes: 28 and 36 inches
Tabletop models of Dobsonian telescopes are the smallest. Tabletop Dobsonians have primary mirrors ranging from 4.5 to 6 inches. These compact telescopes are portable and ideal for beginners or casual observers who want to see celestial objects up close without investing in a larger setup.
Small Dobsonian telescopes range from 6 to 10 inches in aperture. A 6-inch Dobsonian offers a decent light-gathering capacity, making it suitable for viewing brighter celestial objects. An 8-inch model provides better light gathering and resolution, allowing for more detailed observations. A 10-inch Dobsonian strikes a good balance between portability and performance, making it a popular choice among amateur astronomers.
Medium-sized Dobsonian telescopes have apertures between 12 and 16 inches. A 12-inch Dobsonian is an excellent choice for serious amateur astronomers seeking to observe deeper into the cosmos. A 14-inch model offers improved light gathering and detail, while a 16-inch Dobsonian provides exceptional performance for deep-space observation.
Large Dobsonian telescopes come with apertures ranging from 18 to 24 inches. An 18-inch Dobsonian is ideal for advanced amateur astronomers and research purposes. A 20-inch model offers exceptional light gathering and resolution, while a 24-inch Dobsonian is among the largest and most powerful telescopes available in this category.
Finally, extra-large Dobsonian telescopes have apertures between 28 and 36 inches. These telescopes are used by professionals for research and serious astronomy. A 28-inch Dobsonian offers unparalleled light gathering and detail, while a 30-inch model takes it a step further. The 36-inch Dobsonian is one of the largest and most powerful telescopes in the world, providing an incredible view of the farthest reaches of the universe.
Are Orion Dobsonians good?
Orion Dobsonians are praised for their optical quality. They are equipped with a diffraction-limited optical system that delivers clear and sharp images of celestial objects. The Orion SkyQuest XT8 is often recommended for beginners. This model, with its 8-inch aperture, offers an ideal balance between portability and performance, allowing users to observe a wide range of celestial bodies in detail.
Orion Dobsonians are affordable, with the 8-inch model starting at around $300 and the 10-inch model at around $500. The Orion CorrecTension system is a standout feature, enhancing stability by securely holding the telescope tube in place. Orion offers a range of Dobsonian telescopes, with apertures from 6 inches to 12 inches, catering to both beginners and more experienced astronomers.
Are Skywatcher dobsonians good?
Sky-Watcher Dobsonian telescopes are highly regarded as good telescopes. These Dobsonians offer a combination of affordability, ease of use, and high-quality optics, making them a popular choice in the market.
Sky-Watcher Dobsonian telescopes are known for their large apertures, a feature that significantly enhances their light-gathering capabilities. This makes them ideal for observing a wide range of celestial objects, from the Moon and planets to deep-sky objects like nebulae and galaxies. The telescopes are designed with user-friendly features, such as high-quality metal focusers and good mirror quality, which contribute to their ease of use. Their affordability makes them an excellent choice for beginners who want to explore the night sky without breaking the bank.
The Sky-Watcher Dobsonian line includes several models that offer unique benefits. For instance, the 6″ and 8″ Dobsonians provide excellent value and performance, with focal ratios that effectively reduce coma and distortion. The Heritage 100P stands out for its portability and stylish design, while the Skyliner 200P offers a larger aperture for more detailed observations. The SkyQuest series, known for its classic Dobsonian design, strikes a perfect balance between quality, performance, and affordability. These telescopes feature intuitive altazimuth mounts, which allow for smooth and accurate tracking of celestial objects.
Are Apertura dobsonians good?
Apertura Dobsonian telescopes are a good choice. Apertura Dobsonians offer excellent performance and value for both beginners and seasoned amateur astronomers. These telescopes are considered the best within a budget, providing a high-quality observational experience without breaking the bank.
The Apertura Dobsonian AD8 model is renowned for its ability to deliver sharp images of both planets and deep sky objects, making it a popular choice among amateur astronomers. The AD12 model, with its larger aperture, takes the viewing experience a step further by resolving tougher globular clusters and revealing fine details of celestial objects. AD8 and AD13 telescopes are designed with user comfort in mind, offering a comfortable viewing position and a smooth swiveling motion. They come equipped with high-quality accessories such as eyepieces and a finder scope, further enhancing their value.
Apertura Dobsonian telescopes are not only good for beginners due to their affordability but because of their ease of use. They feature a manual altazimuth mount that is simple to operate, making the observational experience less daunting for newcomers. Apertura Dobsonian telescopes are customizable, allowing users to add light shields and other accessories to enhance their viewing experience. The Dobsonian base provides a positive user experience, making these telescopes an excellent choice for anyone looking to buy their first telescope or add to their existing collection on a budget.
Are Celestron Dobsonians good?
Celestron Dobsonians are good telescopes, they offer an excellent balance of quality, performance, and affordability. Celestron Dobsonian telescopes are highly regarded by amateur astronomers for their value and performance. The 8-inch models of Celestron Dobsonians are particularly notable, featuring excellent optics that provide sharp and immersive views of celestial objects. The solid mount, complete with a handle for easy carrying, further enhances the user experience. Celestron Dobsonians come with accessories, including an integrated smartphone app that simplifies celestial navigation, making them user-friendly for beginners.
The StarSense Explorer series of Celestron Dobsonians offers convenience and accuracy, aiding users in aligning their telescopes. The 10-inch model provides a significant upgrade in light-gathering ability, offering better views of faint objects. Celestron Dobsonians are suitable for both beginners and experienced astronomers, proving effective even in light-polluted city locations. Some users mention a premium charge for the StarSense Explorer models and recommend investing in better eyepieces to optimize the viewing experience.
Celestron Dobsonians stand out for their user-friendly design, integrated technology, and overall performance, making them a good choice for amateur astronomers seeking a reliable and efficient telescope.
Are Zhumell Dobsonians good?
Zhumell Dobsonians are good telescopes for beginners. Zhumell Dobsonians are often compared to other popular Dobsonian models like the Orion SkyQuest Classic and Celestron models, and Zhumell Dobsonians consistently rank among the best. The Zhumell Dobsonians’ design focuses on ease of use and setup, making them an excellent choice for those new to astronomy.
One of the standout features of Zhumell Dobsonians is their sturdy, intuitive, and stable mounts. The Dobsonian design provides stable and smooth altazimuth motion, making it easy to track objects in the night sky. Zhumell Dobsonians come with valuable accessories like 1.25″ and 2″ eyepieces and a finder scope, which help beginners start their astronomy journey.
Models like the Z8, Z10, and Z12 are highly regarded for their performance and value. These models have large apertures (8-inch, 10-inch, 12-inch) that provide impressive light-gathering capabilities and clear views of celestial objects. Users and astronomers alike have praised Zhumell Dobsonians for their optical performance and solid construction. Positive reviews often highlight clear views of the Moon, planets, and deep-sky objects, further solidifying Zhumell Dobsonians as a good choice for anyone looking for a high-quality, affordable telescope.
Are Meade Dobsonians good?
Meade Dobsonians are well-regarded and considered good telescopes, offering high-quality optics that provide clear and bright images. Meade Dobsonians are available in both truss and solid tube designs, with the solid tube designs being easier to use due to the absence of assembly requirements. The Lightbridge series is praised for its stability, ease of use, and portability, making it a popular choice among astronomers.
When considering Meade Dobsonians, it’s important to note that some users have reported issues with the laser finder and the quality of the focusers. The mounts that come with these telescopes can sometimes be weak or stiff, which may affect the tracking of celestial objects. Meade Dobsonians are a good choice for those looking for versatile and affordable telescopes, especially for deep sky observations.
IMeade Dobsonians may not be the best choice for astrophotography due to their altazimuth mounts, which can make tracking objects more difficult. You might want to consider a telescope with an equatorial mount, such as those offered by Celestron.
Are Explore Scientific Dobsonians good?
Explore Scientific Dobsonians are highly regarded in the commercial telescope market, often considered some of the best budget-friendly options available. The Explore Scientific Truss Tube Dobsonians, particularly the 10″ and 12″ models, are popular choices due to their smooth focusing, precise machining, and portability, as they can be disassembled for easy transport.
The Explore Scientific Dobsonians offer several advantages that make them stand out. Their large apertures, ranging from 10 to 16 inches, provide impressive light gathering capabilities, making them ideal for both beginners and experienced astronomers in the UK and beyond. The high-quality optics, featuring mirrors made from low-thermal-expansion glass, ensure minimal distortion and excellent image quality. The telescopes are built with robust, powder-coated steel tubes and come with a stable altitude-azimuth mount, although some users opt for equatorial platforms or goto tracking systems for added functionality.
Larger Explore Scientific Dobsonian models are quite heavy, which poses a challenge during transportation. Assembly process of Explore Scientific Dobsonians is time-consuming.
What is a truss tube Dobsonian telescope?
The truss tube Dobsonian telescope is intentionally designed to be portable and easy to assemble. This feature sets it apart from traditional solid tube scopes, which can be cumbersome and challenging to transport. The truss tube design breaks down the telescope into smaller, more manageable parts. This not only makes it easier to store and transport but reduces the overall weight of the telescope, further enhancing its portability.
One of the standout examples of a truss tube Dobsonian telescope is the Explore Scientific Truss Dobsonian. This telescope offers apertures up to an impressive 20 inches and comes equipped with features such as a two-speed focuser and an LED finder. The Explore Scientific Truss Dobsonian boasts a quick cool-down time and is not affected by tube currents, ensuring optimal performance and high-quality views of celestial objects.
The truss tube Dobsonian telescope is a cost-effective choice for amateur astronomers. It is less expensive than other types of telescopes, yet it provides more light for the money, thanks to its large aperture. This combination of affordability and performance makes it an attractive option for those looking to delve into the fascinating world of astronomy without breaking the bank.
What mounts are used with Dobsonian telescope?
The Dobsonian telescope uses a specific kind of mount known as the Dobsonian mount. This mount is essentially a modified version of the altazimuth mount, invented by John Dobson in 1956. The Dobsonian mount is made of wood and consists of a rocker box, a bearing box, and a tube assembly. It provides stable support for Newtonian telescopes, allowing them to move freely in both azimuth and altitude. This mount is particularly popular among amateur astronomers due to its ease of use and setup. It doesn’t require leveling and is primarily used for visual observations, not astrophotography. Unlike other mounts, the Dobsonian mount is not used with tripods; instead, it is used with a wooden base.
Altazimuth mounts are the general type of mounts used with Dobsonian telescopes. These mounts are designed to move in both altitude and azimuth, providing a simple, sturdy, and cost-effective solution for Dobsonian telescopes. The altazimuth mount consists of a rotating platform that allows the telescope to move in azimuth, along with an altitude axis that enables up and down movement. This kind of mount is ideal for visual observing, offering a smooth and intuitive way to track celestial objects.
Some Dobsonian mounts come with motorized systems for tracking celestial objects. These motorized systems allow for smoother and more accurate tracking, enhancing the overall observing experience. Not all Dobsonian mounts feature these motorized systems.
Equatorial mounts are less commonly used with Dobsonian telescopes. Equatorial mounts are designed to track celestial objects as the Earth rotates, providing a different kind of tracking experience compared to altazimuth mounts.
What is a goto Dobsonian telescope?
A Dobsonian telescope equipped with a computerized GoTo system is known as a GoTo Dobsonian telescope. This type of reflector telescope utilizes digital technology to automatically locate and track over 42,000 celestial objects, providing an enhanced stargazing experience. GoTo Dobsonians employ a computerized system that finds and tracks objects, making them the best choice for beginners and experienced astronomers alike.
The optical tube of a GoTo Dobsonian telescope features a rigid, collapsible design, ensuring ease of transportation without compromising structural integrity. One popular example of a GoTo Dobsonian telescope is the Sky-Watcher Flextube SynScan Dobsonian, which combines portability with exceptional performance. GoTo Dobsonian telescopes are highly regarded for astrophotography, as they can accurately track celestial objects, although additional equipment may be necessary for optimal results.
The computerized mount of a GoTo Dobsonian telescope incorporates motors and encoders to automatically slew to and track celestial objects. This digital setting circles system allows users to quickly locate and observe their desired targets using a handheld controller. The extensive database includes thousands of celestial objects, from stars and planets to galaxies and nebulas.
What is altazimuth Dobsonian telescope?
An altazimuth Dobsonian telescope, often simply referred to as a Dobsonian telescope, is a type of reflector telescope that combines the simplicity of a Dobsonian mount with an altazimuth tracking system. This unique combination makes it an excellent choice for both beginners and experienced stargazers alike.
The altazimuth mount is a key feature of the Dobsonian telescope. It allows the telescope to move in two directions: altitude (up and down) and azimuth (left and right). This simple, intuitive movement is similar to how a gun turret works, making it easy to track celestial objects as they move across the sky. The mount is designed for balancing, which makes the telescope easy to move around and track objects smoothly.
One of the unique aspects of using a Dobsonian telescope is that it requires manual tracking. While this might sound hard, it can be a fun and rewarding experience, especially for beginners. To aid in locating objects in the sky, Dobsonian telescopes include setting circles. Some modern versions even come with digital setting circles, making the process of locating celestial objects even easier.
What is equatorial Dobsonian telescope?
An equatorial Dobsonian telescope is an innovative astronomical tool that integrates the advantages of an equatorial mount with the simplicity and affordability of a Dobsonian telescope. This unique combination provides an exceptional observational experience for both amateur astronomers and seasoned stargazers.
The key components of an equatorial Dobsonian telescope include the equatorial mount and the Dobsonian telescope itself. The equatorial mount is a motor-driven platform designed to track celestial objects accurately. It compensates for the Earth’s rotation by aligning its polar axis with the Earth’s rotational axis, which is approximately 23.5° from the celestial equator.
The equatorial mount allows for the smooth and accurate tracking of celestial objects, which is particularly beneficial for extended observation sessions. By combining the equatorial mount with the Dobsonian telescope, one can achieve a stable and precise platform for both visual observations and astrophotography.
What is a collapsible Dobsonian telescope?
The collapsible design of the Dobsonian telescope allows it to be transported in two compact pieces, making it an ideal choice for astronomers on the go. The telescope uses a truss tube design, which breaks the tube into smaller, interconnected pieces. This design allows the telescope to be easily collapsed and stored when not in use.
Many collapsible Dobsonian telescopes come with a computerized GoTo system, which allows for easy tracking of celestial objects. The Skywatcher brand is a well-known manufacturer of collapsible Dobsonian telescopes, offering a range of models to suit different needs and budgets.
Collapsible Dobsonian telescopes are ideal for deep sky observation and astrophotography. They often feature a light shroud to reduce stray light and improve contrast, resulting in clearer and more detailed images of celestial objects. The large aperture and fast focal ratio of these telescopes make them best suited for low power observation of large and faint objects such as nebulae and galaxies.
What is a Dobsonian telescope with tracking?
A Dobsonian telescope with tracking is a refined version of the traditional Dobsonian telescope, integrating a motorized tracking system to enhance the observer’s experience. Dobsonian can be equipped with a tracking system. An equatorial mount or a tracking platform is added to the Dobsonian telescope, enabling it to compensate for the Earth’s rotation. This feature is particularly important when observing objects high in the sky or for extended periods, as it allows the telescope to continuously point at a celestial object as it moves across the sky.
The motorized tracking system replaces or upgrades the traditional manual altazimuth mount with a computerized system. This system includes motorized drives with electric motors that slowly rotate the telescope’s axes, compensating for the Earth’s rotation. The system features computerized control using astronomical software and sensors to guide the motors, ensuring accurate tracking of the desired object.
The integration of a tracking system into a Dobsonian telescope offers several benefits. It allows for longer and more comfortable observing sessions, as the observer no longer needs to constantly adjust the telescope’s position. Tracking system requires minimal manual intervention, making the observing experience more enjoyable. This setup is suitable for both visual observation and astrophotography, expanding the possibilities for amateur astronomers.
What is a motorized Dobsonian telescope?
A motorized Dobsonian telescope is a reflecting telescope that has been enhanced with automated movement. This type of telescope is mounted on a Dobsonian mount, an alt-azimuth type of mount known for its simplicity and ease of use.
Motorized versions of Dobsonian telescopes use a motor drive and computerized controller to automate this process. The motor drive and controller work together to automatically locate and track celestial objects, making it easier for amateur astronomers to observe and image the night sky.
Motorized Dobsonians are capable of locating and centering over 42,000 celestial objects with pushbutton ease. This is a significant advantage over manual Dobsonian telescopes, which can be hard to move and adjust precisely. The motorized system allows for smooth and precise tracking of celestial objects, making it easier to observe and image objects over extended periods. This is particularly useful for astrophotography, as well as for observing objects that move rapidly across the sky, such as planets and comets.
For those who already own a Dobsonian telescope, it is possible to add a motor drive to the existing telescope. Various designs and kits are available for those interested in building their own motorized Dobsonian. The automation is achieved through the use of electric motors and control systems that drive the telescope’s altitude and azimuth axes, providing smooth and precise movement for tracking celestial objects.
What is a tabletop Dobsonian telescope?
A tabletop Dobsonian is a compact and lightweight telescope, making it ideal for placement on a table or any flat surface.
One of the standout features of the tabletop Dobsonian telescope is its collapsible tube assembly. This feature makes the telescope highly portable and easy to store. The aperture of these telescopes can range from 4.5 inches to 150mm, making them a good choice for both beginners and seasoned astronomers.
Some models of tabletop Dobsonian telescopes come with addons such as a finder scope, laser collimator, or even computerized tracking systems. These features complement the telescope’s basic design, enhancing its functionality and making it even more user-friendly.
Brands like Zhumell, Orion, and SkyWatcher offer some of the best tabletop Dobsonian telescopes in the market. These telescopes are often recommended for beginners due to their ease of use, affordability, and high-quality optics. Some models even integrate with smartphones, allowing users to analyze the night sky and locate specific objects with ease.
What is the difference Dobsonian and Newtonian telescope?
The primary difference between a Dobsonian and a Newtonian telescope lies in their mounting systems. A Dobsonian telescope is a type of Newtonian telescope that employs a specific altazimuth mount, which is known for its simplicity and affordability.
Newtonian telescope utilizes various mounts, including equatorial mounts. This versatility allows for a range of observational approaches. The mount does not define the Newtonian telescope; rather, it is characterized by its optical design. This design includes a concave primary mirror that gathers and focuses light, and a flat diagonal mirror that directs this light into an eyepiece for the observer.
Dobsonian telescope maintains the same optical design as a Newtonian telescope but is distinct due to its unique mount. The Dobsonian mount is a simple, low-cost altazimuth mount that moves in two axes: altitude (up and down) and azimuth (left and right). This design makes it user-friendly, contributing to its popularity among amateur astronomers.
The Dobsonian telescope is known for its ease of use. Its design prioritizes simplicity, making it an ideal choice for beginners or those seeking a straightforward observational experience. This simplicity extends to the cost as well; Dobsonian telescopes are less expensive than Newtonian telescopes with equatorial mounts due to their more affordable mounting systems.
Dobsonian telescopes often prove to be more portable than their Newtonian counterparts. Their simpler design and lighter weight contribute to this portability, making them a convenient option for those who may need to transport their telescope for stargazing sessions.
Dobsonian telescopes have gained significant popularity among amateur astronomers. Their affordability, ease of use, and portability make them an attractive choice for those looking to explore the night sky without the complexity and cost associated with some other telescope designs.
What is the difference Dobsonian vs refractor telescope?
Dobsonian and refractor telescopes are two popular types of telescopes among amateur astronomers, each with its unique advantages and disadvantages. The primary difference between these two telescopes lies in their optical design.
A Dobsonian telescope, known as a Newtonian reflector, uses a concave mirror to gather and focus light. This design allows for a larger aperture, making it an excellent choice for observing deep-sky objects such as galaxies and nebulae. Dobsonians are more affordable than refractors of similar aperture, making them a popular choice for beginners and those on a budget. One of the standout features of Dobsonian telescopes is their collapsible design, as seen in models like the SkyWatcher Skyliner, which makes them relatively easy to transport despite their larger size. Dobsonians require regular collimation, or alignment of their mirrors, to maintain optimal performance.
A refractor telescope uses a convex lens to gather and focus light. Refractors are known for their high-contrast images and good color correction, making them ideal for planetary observation. They require little to no maintenance as the lens is fixed in place. Refractors are often more compact and portable than Dobsonians, making them a great alternative for those who value portability. Refractors can suffer from chromatic aberration, especially at larger apertures, which can cause color fringing around objects.
Dobsonian telescopes are mounted on a simple, manual altazimuth mount. This design contributes to their ease of use and affordability. Refractors can be mounted on various types of mounts, including equatorial and altazimuth, providing more flexibility but potentially adding to their cost.
What mirror does Dobsonian telescope have?
A Dobsonian telescope operates with a single, large, concave primary mirror. The shape of this mirror is crucial as it collects and focuses light from distant celestial objects, providing clear and detailed images of the night sky.
The primary mirror in a Dobsonian telescope is securely fixed in place. The secondary mirror, which is significantly smaller, can be manually adjusted. This adjustment is known as collimation, a process essential for aligning the mirrors correctly to ensure optimal performance of the telescope.
What eyepieces are used with Dobsonian telescope?
Dobsonian telescopes use a variety of eyepieces such as Plossl, Kellner, and Erfle. These eyepieces are designed to work seamlessly with the Dobsonian design, enhancing the viewing experience for both beginners and seasoned astronomers.
Plossl eyepieces are often included with Dobsonian telescopes due to their versatility and reliability. They feature a 1.25-inch diameter and offer a field of view ranging from 52 to 55 degrees. This makes them an excellent choice for a wide range of astronomical observations.
Kellner eyepieces are another popular choice for Dobsonian telescopes. They have a 1.25-inch diameter but provide a slightly narrower field of view, between 44 and 50 degrees. Despite the smaller field of view, Kellner eyepieces are appreciated for their sharp images and robust construction.
Erfle eyepieces, while not as common, are sometimes used with Dobsonian telescopes. They offer the widest field of view among the three, ranging from 60 to 70 degrees. This makes them ideal for observing large celestial objects or expansive star fields.
For beginners in astronomy, SVbony Goldline or Redline eyepieces are often recommended due to their decent quality and wide field of view. Specific eyepiece recommendations include 4mm and 7mm eyepieces for lunar and planetary observation, a 16mm eyepiece for general viewing, and a 30-35mm 2″ eyepiece for wide field use.
How much does a Dobsonian telescope cost?
The cost of a Dobsonian telescope can vary greatly, depending on the size of the aperture and the quality of the components. A 6-inch budget Dobsonian telescope can be purchased for around $167, making it a cheap yet effective option for stargazing.
A portable Dobsonian telescope costs around $300-$800. A 6-8 inch (15-20 cm) aperture reflector telescope is a good starting point for beginners. These telescopes offer a good balance between portability and light-gathering power, making them the best complement for those who want to explore the night sky without breaking the bank.
Prices for 8-inch Dobsonians have been increasing due to demand, with some models now selling for around $600 or more. A 10-inch Dobsonian can cost around $600 or more, while a 12-inch Dobsonian can cost around $600 or more, with some models exceeding $1,000. These big telescopes offer impressive views of faint deep sky objects, such as nebulae, but they may not be as portable as smaller models.
Advanced Dobsonian telescope price can range from $1,000-$3,000 or more. These telescopes have larger apertures and higher-quality components, such as precision-ground mirrors and high-end eyepieces.
Is it safe to buy a used Dobsonian telescope?
Yes it can be safe to buy a used Dobsonian telescope. You should inspect the instrument before making the purchase. The key to ensuring a successful transaction lies in thoroughly examining the telescope’s mechanical and optical components, as well as verifying the inclusion of necessary accessories.
When considering a used Dobsonian telescope for sale, begin by assessing its mechanical condition. Carefully examine the altitude and azimuth bearings, ensuring they move smoothly without any signs of wear or damage. Optical quality is another crucial factor; inspect the primary mirror for any scratches, cracks, or signs of deterioration. Verify that the telescope is properly collimated, as correct mirror alignment is vital for optimal image quality.
Ensure the mount is stable and capable of supporting the telescope’s weight, as a sturdy mount is essential for smooth tracking and clear images. Check if the telescope comes with necessary accessories such as an eyepiece, finder scope, and star diagonal. Researching the market value and comparing prices is important to guarantee a fair deal. Lastly, consulting an expert and deciding on your budget before purchasing can help you make an informed decision.
Can you make a Dobsonian telescope at home?
Yes, you can make a Dobsonian telescope at home. The Dobsonian telescope, known for its simplicity and affordability, was originally designed to be a homemade telescope. To build your own Dobsonian telescope, you will need a few key components.
The primary components needed for making a Dobsonian telescope include a parabolic mirror with a diameter of at least 6 inches and a focal length of around 48 inches, a sturdy altazimuth mount made of wood, metal, or a combination of both, and a cardboard or PVC tube with a diameter of 12-18 inches and a length of 48 inches to hold the mirror and eyepiece in place. You will need a telescope eyepiece with a focal length of around 20-30 mm and a small telescope or sighting tube to help aim the main telescope at celestial objects.
To assemble your homemade Dobsonian telescope, begin by attaching the mirror to the mount using a mirror cell and a set of screws. Next, attach the tube to the mount using screws or tube rings. Install the eyepiece and finder scope on the tube, and align the mirror and eyepiece using a laser collimator or sighting tube. With your homemade Dobsonian telescope, you can expect to see the Moon’s surface features, planets such as Jupiter’s cloud bands and Saturn’s rings, and deep-sky objects like star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies.
Where to find Dobsonian telescope plans for diy?
You can find plans for diy Dobsonian in the following resources.
- Books: Two highly recommended books for Dobsonian telescope making are “The Dobsonian Telescope” by David Kriege and Richard Berry, and “The Dobsonian Telescope Handbook.” Both books provide detailed plans, instructions, and tips for building a Dobsonian telescope. The plans in these books can be scaled to different sizes, allowing you to build a telescope that suits your specific needs and preferences.
- Websites: Several websites offer valuable resources for building a Dobsonian telescope. Scopemaking.net provides a range of plans and resources to help you get started. Stellafane, a website dedicated to amateur telescope making, features a homemade telescope gallery that can inspire and guide your project. The Dobson Making website offers resources for building both motorized and non-motorized Dobsonian telescopes. For those interested in building a lightweight Dobsonian, the DIY Telescope Project website hosts the Ultraportable Dobsonian Build Series, which provides plans and ideas for your project. Additionally, the 12inch Dobsonian Telescope website offers plans and ideas specifically for building a 12-inch Dobsonian telescope.
- Forums: Forum communities can be a great source of information and support during your Dobsonian telescope building journey. The Cloudy Nights forum is a popular resource for amateur telescope makers, offering advice and plans for building a Dobsonian telescope.
- DIY Project Platforms: Instructables, a DIY project sharing platform, features a detailed guide called Mariner for building a Dobsonian telescope. This guide includes step-by-step instructions and photos to help you through the building process.
- Official Resources: John Dobson’s official website is another excellent resource for Dobsonian telescope making. The website provides plans, instructions, and tips for building a Dobsonian telescope at home.
- Commercial Kits: If you prefer to use precision-machined parts for your Dobsonian telescope, consider the Orion Telescope Dobsonian kit. This kit includes precision-machined aluminum and carbon fiber parts, making it easier for you to build a high-quality Dobsonian telescope.
When building a Dobsonian telescope, remember to carefully follow safety guidelines and building instructions to ensure a successful and functional outcome. Happy building!
Is Dobsonian telescope good for astrophotography?
Dobsonian telescopes can be used for astrophotography, but they come with certain limitations that may affect the quality of pictures taken. Dobsonian telescopes are popular for visual astronomy, especially for observing the Moon and planets, due to their large apertures and low costs.
The primary issue lies in the Alt-Az mount used by Dobsonian telescopes, which is not ideal for long exposure images. This mount does not compensate for the Earth’s rotation, leading to star trails in images. While some Dobsonian telescopes may offer an optional equatorial tracking system, these often lack the precision of dedicated equatorial mounts. The tracking performance can be poor, making it challenging to capture high-quality images at home or in a professional setting.
Despite these challenges, it is possible to make good use of a Dobsonian telescope for astrophotography by following some practical tips. Using a camera with short exposure times, between 10-30 seconds, can help minimize tracking errors. A wide-angle lens or camera can reduce the impact of tracking errors. It’s recommended to focus on bright objects such as the Moon, planets, or star clusters, as these are easier to capture. Using image processing software can significantly improve the quality of your pictures by reducing noise and aligning multiple frames.
What can you see with a Dobsonian telescope?
With a Dobsonian telescope, you can see a variety of celestial objects. Dobsonian is often referred to as a “light bucket,” allows you to observe the Moon, planets, stars, constellations, and deep-sky objects (DSOs) such as galaxies, nebulas, and star clusters in great detail.
The Moon appears bright and clear through a Dobsonian telescope, revealing surface features such as craters and mountains. Planets like Jupiter, Saturn, Venus, and Mars are visible. With Jupiter, you can see its moons and cloud bands, while Saturn’s rings and moons, like Titan and Rhea, are visible. The phases of Venus and surface features on Mars during opposition can be observed.
Individual stars and constellations can be seen in stunning detail with a Dobsonian telescope. You can observe double star systems, multiple star systems, and asterisms. The larger the aperture size of your Dobsonian telescope, the more stars and fainter objects you can see.
Deep-sky objects such as galaxies, nebulas, and star clusters are within reach of a Dobsonian telescope. You can see the Andromeda Galaxy (M31), the Orion Nebula (M42), and the North America Nebula (NGC 7000). Star clusters like the Pleiades Cluster (M45) and the Hyades Cluster are visible.
How far can a Dobsonian telescope see?
The distance a Dobsonian telescope can see is primarily determined by its size, specifically the diameter of its primary mirror. Given the right conditions and a good quality telescope, these instruments can offer remarkable views of distant objects in space.
An 8-inch Dobsonian telescope can reach a maximum distance of around 300-400 million light-years. This range allows for the viewing of various distant objects such as galaxies and nebulas, offering a fascinating glimpse into the far reaches of the universe.
A 16-inch Dobsonian telescope can observe objects approximately 1-2 billion light-years away. This extended reach enables the observation of even more distant and faint objects in space, providing a more comprehensive view of the cosmos.
A 24-inch Dobsonian telescope could observe objects up to an astonishing 4-6 billion light-years away in theory. This distance is roughly halfway to the edge of the observable universe, making it possible to view some of the farthest objects within our reach.
Is Dobsonian telescope for beginners?
Dobsonian telescopes are an excellent choice for beginners due to their ease of use, affordability, and impressive performance. These telescopes are often considered the best option for those new to astronomy, offering great value for their price.
Dobsonian telescopes are known for their intuitive design and simple altazimuth mount, making them easy to set up and use. The simplicity of their design makes them a popular choice for beginners who want to avoid the complications of other types of telescopes. Dobsonians are affordable, making them accessible for those on a budget. A 6-inch Dobsonian is a good starting point for beginners, while an 8-inch model offers better light-gathering capabilities.
Dobsonians are ideal for visual observations of the night sky but are not suitable for astrophotography or terrestrial viewing. They are not equipped with tracking motors, making them less ideal for long-exposure astrophotography. Recommended brands for beginners include Orion, Apertura, and Sky-Watcher.
Do you need a light shroud for Dobsonian telescope?
Creating a light shroud for a Dobsonian telescope can significantly enhance your stargazing experience, although it’s not an absolute necessity. A light shroud, essentially a collapsible cover made of opaque black fabric, is designed to block out stray light that can infiltrate the telescope tube. This unwanted light can adversely affect image contrast and clarity, making it difficult to observe faint celestial objects. By reducing glare and enhancing contrast, a light shroud can markedly improve the overall quality of your observations.
Dobsonian telescope users, particularly those employing commercial truss-tube models such as Meade, Orion, and Sky-Watcher, often find themselves observing the night sky from locations with nearby artificial lighting. Light shroud serves the dual purpose of preventing dust accumulation and dew formation on the mirrors, thereby ensuring optimal performance of your telescope. Shroud may not be essential if you conduct your observations from a dark location. The elastic bands fitted around the telescope tube make it easy to attach and remove the shroud as per your observing conditions.
How to collimate a Dobsonian telescope?
Collimating a Dobsonian telescope is a process that ensures the primary and secondary mirrors are aligned correctly, providing the best possible image quality. While using a laser collimator can make the process easier, it is possible to collimate your Dobsonian telescope without one.
To begin, prepare your telescope by setting it up in a dark location with minimal vibrations. Remove any eyepieces, star diagonals, or other accessories, and ensure the telescope is at room temperature to prevent thermal expansion or contraction. Identify the collimation points on your telescope: the primary mirror cell at the bottom, the secondary mirror holder at the top, and the focuser where the eyepiece is attached.
If you have a laser collimator, insert laser into the focuser and turn it on to project a beam onto the primary mirror. If you don’t have a laser collimator, you can use a collimation cap or Cheshire sight tube instead. Adjust the primary mirror’s tilt and rotation using a screwdriver or Allen wrench until the reflection of the focuser or laser beam is centered on the primary mirror. Tighten the locking screws to secure the primary mirror in place.
Collimate the secondary mirror by loosening the secondary mirror holder’s locking screws and adjusting the mirror’s tilt and rotation. If using a laser collimator, ensure the laser beam is centered on the primary mirror. Center the reflection of the primary mirror in the secondary mirror and tighten the locking screws to secure the secondary mirror.
Verify collimation, remove the collimation tool and attach an eyepiece. Observe a bright star or distant object through the eyepiece and check for any signs of misalignment, such as elliptical star shapes or uneven illumination. If you notice any misalignment, repeat the collimation process until the image is sharp and symmetrical.
When collimating your Dobsonian telescope, it’s best to do so on the side of the sky where you will be observing. Check collimation again if you pass the meridian, as the telescope’s components can shift over time. If you’re using a laser collimator, ensure it is collimated before use. Collimating during the day can provide better visibility of the laser beam or star images. For optimal results, use a high-quality laser collimator specifically designed for Dobsonian telescopes.
How does a Dobsonian telescope work?
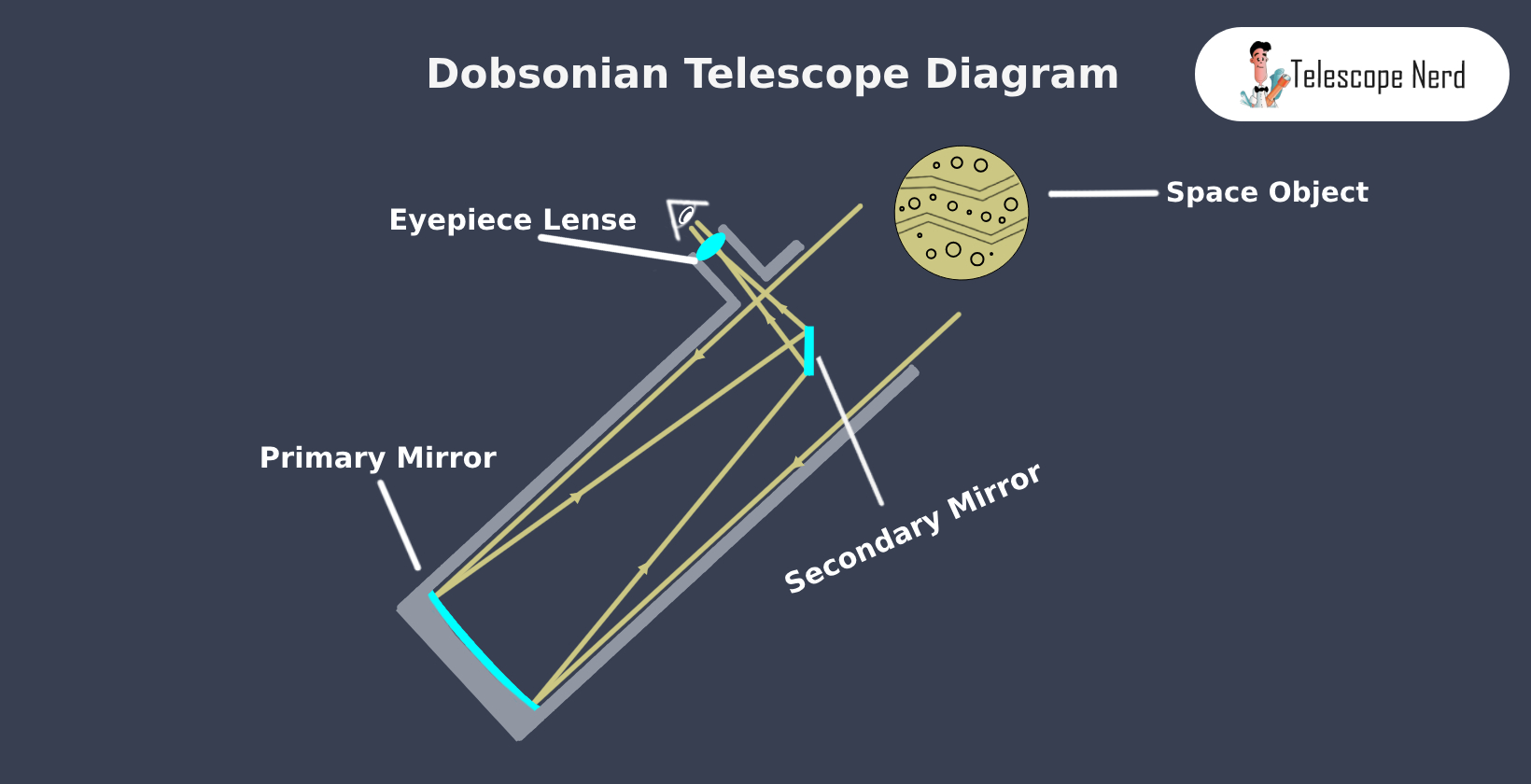
A Dobsonian telescope works by utilizing a primary mirror to gather and focus light from celestial objects. The primary mirror, made of glass, is concave and paraboloid-shaped, with a reflective coating to enhance light collection. This mirror is mounted at the bottom of a tube and reflects the gathered light upwards to a secondary mirror.
The secondary mirror, usually a small, flat mirror, plays a crucial role in the functioning of Dobsonian telescopes. It is strategically positioned to redirect the light from the primary mirror to the eyepiece. The eyepiece, in turn, magnifies the image, allowing the observer to view the celestial object in detail.
Dobsonian alt-azimuth mount design allows for easy movement and pointing at objects in the sky. Dobsonian telescopes require manual tracking of objects as they move across the sky, which some users might find challenging.
What parts does Dobsonian telescope have?
Dobsonian telescope has the following parts.
- Optical Tube Assembly (OTA).
- Primary mirror.
- Secondary mirror.
- Eyepiece.
- Base or rocker box.
- Finderscope.
- Focuser.
The primary parts of a Dobsonian telescope can be categorized into the Optical Tube Assembly (OTA) and the base, known as the rocker box. The OTA is essentially the light bucket of the telescope, which houses the primary mirror, secondary mirror, and the eyepiece. The primary mirror, made of glass or acrylic, is the most crucial component of the OTA. It is a concave mirror that collects and focuses light from distant objects. The shape and cleanliness of the primary mirror significantly impact the telescope’s performance. Some enthusiasts even opt for homemade Dobsonian telescopes, using mirror shaving techniques to create their own primary mirrors.
The secondary mirror is a smaller, flat mirror mounted on a sling or a spider vanes system. Its role is to redirect the light gathered by the primary mirror to the eyepiece. The eyepiece is a removable lens that magnifies the focused light from the mirrors, allowing the user to observe the object. A laser collimator can be used to align the primary and secondary mirrors for optimal performance.
The base or rocker box of a Dobsonian telescope is a sturdy stand that supports the OTA and allows smooth movement in altitude (up/down) and azimuth (left/right) directions. This design, known as an altazimuth mount, makes it easy to install and use the telescope, even for beginners. Unlike equatorial mounts, Dobsonian bases do not offer tracking capabilities, but they are portable and provide a simple system for manual pointing.
Dobsonian telescopes may include several add-ons depending on the model. A finderscope is a small, auxiliary telescope attached to the main telescope to help locate objects in the night sky. A focuser is a mechanism that holds the eyepiece in place and allows for adjustments to achieve a sharp focus. Some models, like the Zhumell Dobsonian, may include additional features such as a counterweight system for balance, a latitude adjustment mechanism, or a Teflon bearing system for smooth motion.

