Telescope Focal Length: Explanation
Focal length is the distance between the objective lens or mirror of a telescope and the point where incoming light converges to form an image. Knowing the focal length allows observers to comprehend key aspects of a telescope’s performance. To calculate the focal length of a telescope or lens, measure the distance from the lens or mirror to the image formed when parallel light rays are focused. This distance directly determines the telescope’s magnification and field of view, making it a fundamental concept for any observer. Additionally, focal length is a crucial factor in determining the telescope’s focal ratio (f ratio), which influences image brightness and the field of view.
What is Focal Length in a Telescope?
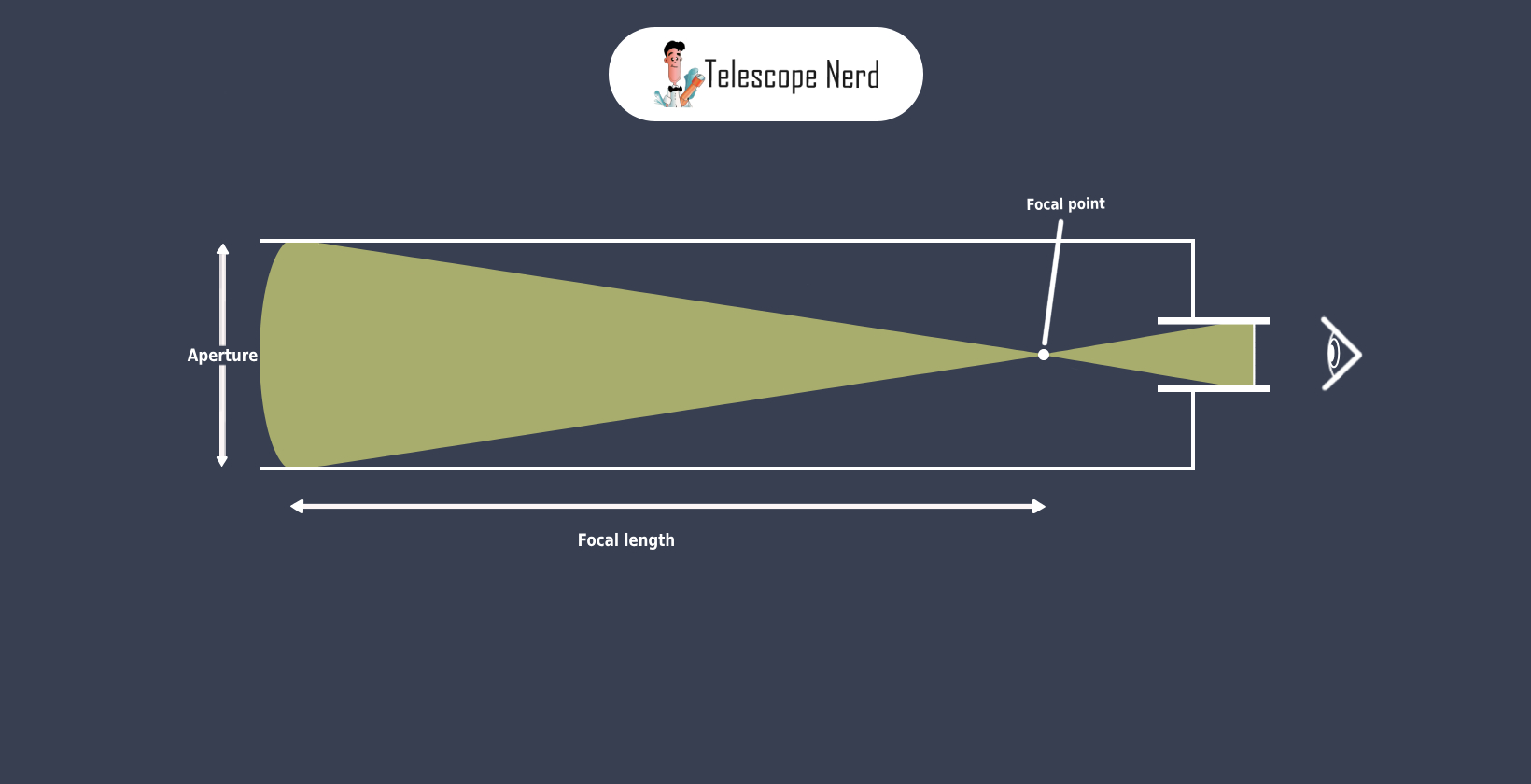
Focal length is the distance between the objective lens or mirror, and the focal point. The focal point is where incoming light converges inside the telescope to form a clear image. The focal length determines the telescope’s magnification power and affects the field of view. A longer focal length results in higher magnification and a narrower field of view, while a shorter focal length provides wider fields of view and lower magnification.
Focal length plays a crucial role in the telescope’s performance and observing capabilities. This value influences the telescope’s ability to resolve details and determines the image’s size and brightness. For planetary and lunar observations requiring higher magnification, focal lengths of above 1000mm are preferred. Shorter focal lengths, under 500mm, are suitable for capturing broader views and astrophotography. Focal lengths between 500mm and 1000mm are most common, as they strike a balance between magnification and field of view.
Focal length is measured in millimeters (mm) and is determined by measuring the distance from the objective to the focal point. How to increase focal length? To increase the focal length range, additional optical elements like Barlow lenses or focal extenders can be used.
Focal length helps with understanding the telescope’s performance and optimizing it for specific observing needs. By knowing the focal length, observers can also calculate the magnification and focal ratio, allowing them to better understand their viewing experience.
How to Calculate Telescope Focal Length?
To calculate a telescope’s focal length, you should measure the objective focal ratio and aperture diameter. Focal length is calculated by multiplying the focal ratio by the aperture size. The formula for calculating focal length is given below.
Focal Length of Telescope = Focal Ratio x Aperture Diameter
For example, if a telescope has a focal ratio of f/10 and an aperture size of 50mm, the focal length of the telescope will be 500mm. There are multiple additional methods to calculate the focal length, including direct measurement or multiplying the magnification by the focal length of the primary optic or using a telescope focal length calculator.
Understanding the telescope’s focal length is crucial for selecting suitable eyepieces to achieve desired levels of magnification and optimizing the telescope for specific observations. The relationship between telescope focal length and objective focal length directly affects the telescope’s magnification power and field of view, providing essential information for a rewarding stargazing experience.
How to Find Focal Length for the Eyepiece of Telescope?
To find the focal length, look at the side of the eyepiece. Telescope manufacturers will typically print or engrave the measurement. If it is not visible, inspect the packaging or contact the manufacturer. The eyepiece is the lens that the observer looks through in a telescope. The focal length of the eyepiece, usually measured in millimeters, determines the telescope’s magnification power and field of view.
Why would an observer want to determine the focal length of their eyepiece? Understanding the focal length of the eyepiece is crucial because it directly affects the magnification of a telescope. Higher magnification might seem preferable, but it’s important to remember that as magnification increases, the brightness and field of view decrease.
How Does Telescope Focal Length Affect Magnification?
Telescope focal length directly affects magnification, the longer the telescope’s focal length, the higher the magnification with a specific eyepiece. Conversely, a shorter telescope focal length results in lower magnification. Understanding this relationship is crucial for telescope users, as it allows them to control and adjust the magnification level based on their observational goals.
Magnification in a telescope refers to the comparison of an observed object’s apparent size through the telescope to its size when viewed with the naked eye. This value is determined by the ratio of the telescope’s focal length to the eyepiece’s focal length. A higher magnification value means that the object appears larger, while a lower magnification provides a wider field of view.
How to calculate telescope magnification from focal length? To calculate telescope magnification from focal length, use the following formula.
Magnification = Telescope Focal Length / Eyepiece Focal Length
For example, if a telescope has a focal length of 1000mm and an eyepiece with a focal length of 20mm, the magnification will be 50 times. Calculating telescope magnification is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps astronomers select the appropriate eyepieces to achieve desired levels of magnification for specific observations. For example, higher magnification is useful for observing details on the Moon and planets, while lower magnification is better suited for capturing extended objects like star clusters and galaxies.
For astrophotography, understanding magnification is essential. It allows photographers to calculate the image scale and field of view when capturing celestial objects with cameras attached to telescopes. The focal ratio (f ratio) is also related to magnification. A lower focal ratio (e.g., f/4) results in a faster telescope with lower magnification and wider fields of view. In contrast, a higher focal ratio (e.g., f/10) provides a slower telescope with higher magnification and narrower views.
How Does Telescope Focal Length Affect Focal Ratio?
The focal length is a factor of focal ratio, therefore an increase in focal length increases the telescope focal ratio. This is because the focal ratio is the relationship between a telescope’s focal length and aperture diameter. This ratio is commonly referred to as the “f/number” or “f ratio”, and is a significant characteristic used to describe telescopes and their optical systems. For instance, an f ratio of f/4 signifies that the focal length is four times the aperture diameter, while an f ratio of f/10 means the focal length is ten times the aperture diameter. Therefore, the focal ratio and focal length are not the same.
The focal ratio plays a crucial role in determining the brightness and speed of a telescope’s optics. A lower f ratio indicates a faster telescope, meaning it gathers more light in a shorter time, making it suitable for capturing faint celestial objects or conducting astrophotography. This results in wider fields of view, allowing astronomers to observe larger regions of the night sky. On the other hand, a higher f ratio characterizes a slower telescope, which captures less light in comparison but offers higher magnification capabilities. Telescopes with higher f ratios are beneficial for observing fine details on celestial objects such as planets and the Moon, providing astronomers with more focused and detailed views. Understanding the focal ratio is essential for telescope users as it directly influences the telescope’s light-gathering capability and its observing characteristics.
Why is Focal Length Important for Telescopes to Work?
Knowing the focal length is important to understand how telescopes work because it determines the magnification and field of view of the telescope. The focal length is the distance between the objective lens or primary mirror and the point where the light converges to form an image (the focal point).
A longer focal length allows the telescope to achieve higher magnification, making distant objects appear larger. This is crucial for observing celestial objects that are far away and appear small to the naked eye. Higher magnification enables astronomers to study the fine details and features of these objects. A shorter focal length provides a wider field of view. This means the telescope is able to observe a larger portion of the sky at once, making it easier to locate objects and track their movements. A wider field of view is especially useful for finding specific targets or for observing large celestial events like meteor showers or eclipses.

