UY Scuti: Meaning, Size, Facts, Fate, Life Cycle
UY Scuti is a variable, red supergiant star. UY Scuti is one of the largest known stars in the Milky Way Galaxy, and it is a dust-enshrouded bright red supergiant. UY Scuti is the biggest star known in terms of sheer physical size, and has a radius 1,708 times that of the Sun. The star is massive enough to end its life as a fiery supernova.
What is the UY Scuti star?
The UY Scuti star is the 38th variable star of the constellation Scutum, and it is a red supergiant star. UY Scuti is called in accordance with the international standard for designation of variable stars, and it is the biggest star in the universe. UY Scuti is a pulsating variable star, and it is located a few degrees north of the A-type star Gamma Scuti.
UY Scuti is a “metal-rich” star. BD-12°5055 is another name for UY Scuti, which is located in the constellation Scutum. The star resides approximately 5,871 light years away from Earth. Stars with a large enough mass transform into red supergiant stars, and UY Scuti belongs to this category. It is one of the largest known stars and is classified as a pulsating variable star. UY Scuti exhibits characteristics typical of variable stars, and its classification includes the term pulsating variable.
What is the history of UY Scuti?
The history of the UY Scuti starts with its cataloguing in 1860, and it was discovered at the Bonn Observatory by German astronomers. Astronomy Magazine reported UY Scuti was cataloged in 1860 for the Bonner Durchmusterung Stellar Catalogue. This catalogue was created by J.C. Müller and P.R.. UY Scuti is located in the constellation Scutum and is classified as a red supergiant star. As a variable star, it belongs to the category of one of the largest known stars. UY Scuti was better documented in 2012, confirming its status as a supergiant star and one of the largest known stars.
How big is the UY Scuti?
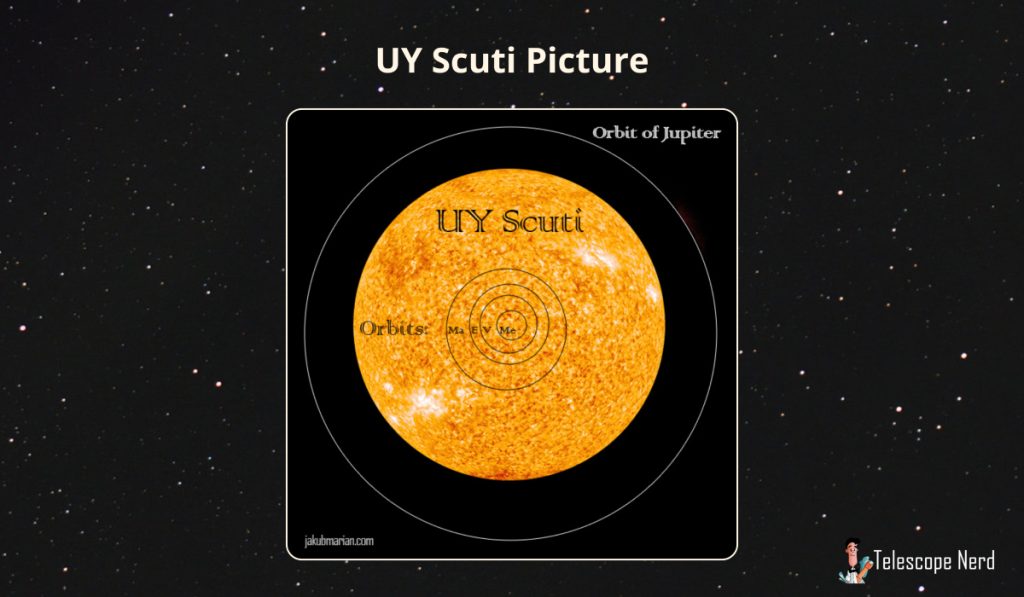
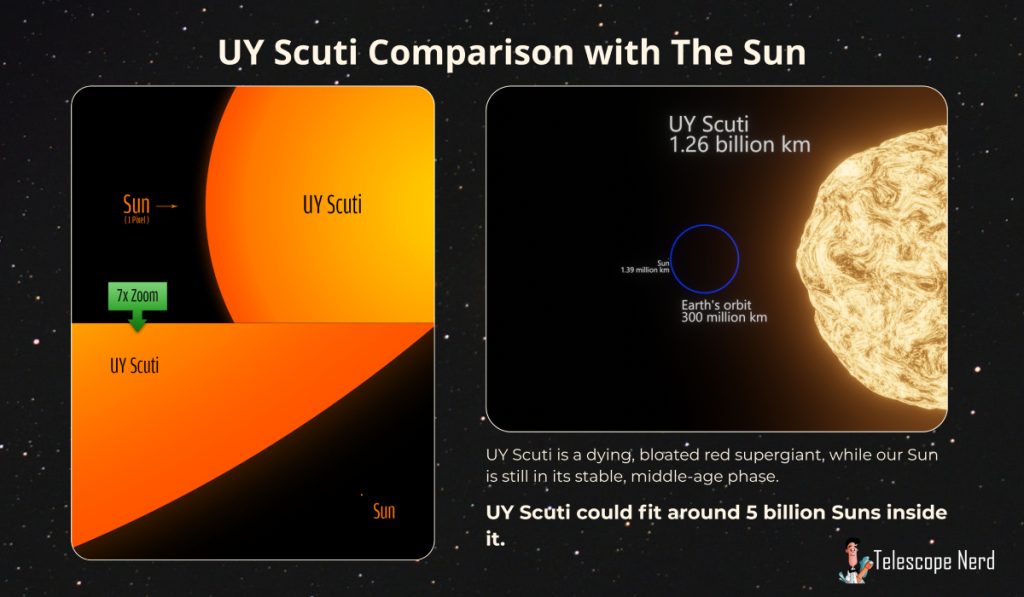
The UY Scuti is approximately 1,700 times larger than our Sun, and it resides in the constellation Scutum. This star is the biggest star known. UY Scuti has a radius of 1.188 × 10^9 ± 134,000,000 km (738,249,485 ± 83,261,461 mi), and its diameter measures approximately 2.4 billion kilometers (1.491 billion miles).
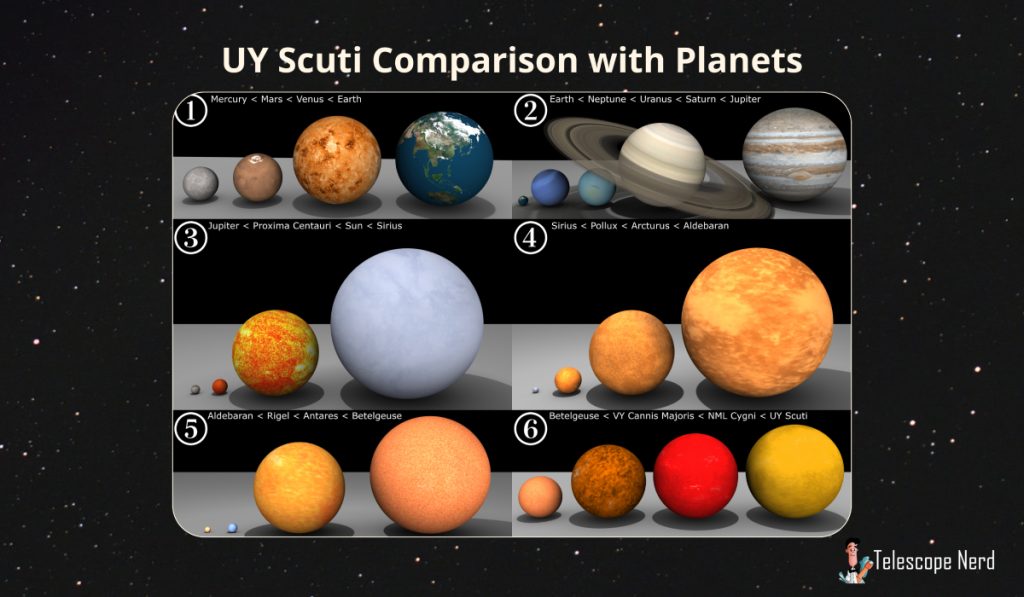
The star has an estimated radius of 1.188 billion kilometers, and its main-sequence radius is about 1,188 million kilometers. UY Scuti has an angular diameter of 5.48 ± 0.10 mas, and its radius is nearly equivalent to that of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. UY Scuti is over 300,000 times brighter than the Sun, yet it tips the scales at between 7 and 10 solar masses. UY Scuti could easily contain over 5 billion Suns, 7 trillion Jupiters, and it could fit 7 quadrillion Earths. It is the largest known star.
What are the facts about UY Scuti?
The facts about UY Scuti are presented below.
- UY Scuti is one of the largest stars in the Milky Way
- UY Scuti is a variable, red supergiant star
- UY Scuti has a luminosity of about 124,000 times more than the Sun
- UY Scuti is located in the constellation Scutum
- UY Scuti is located 5,871 light years away
- UY Scuti has an apparent magnitude of 11.2 and an absolute magnitude of -6.2
- UY Scuti is too far and too dim to be seen from Earth with the naked eye
- UY Scuti has a stellar classification of M4Ia
- UY Scuti has a spectral type of M2-M4Ia-Iab
- UY Scuti is located two degrees north of the white magnitude 4.67 star Gamma Scuti
- UY Scuti is located near the center of the Milky Way
- UY Scuti has a surface temperature of 3,550 K
- UY Scuti has no known companion star
- The stellar parameters of UY Scuti are difficult to determine with a high degree of certainty
- UY Scuti is located in the Cygnus rift
- UY Scuti is located in the Zone of Avoidance
- UY Scuti is enshrouded in dust
- UY Scuti is losing a large amount of mass through stellar winds
- UY Scuti is located northeast of the Eagle Nebula
- UY Scuti is not a particularly bright star in our night sky
- UY Scuti is surrounded by a dense starfield
- UY Scuti would sit beyond the orbit of Jupiter if it replaced the Sun in the Solar System
- UY Scuti is located close to Sagittarius A
- UY Scuti straddles the borderline between a big pair of binoculars and a small telescope
- UY Scuti is cooler than the Sun
- UY Scuti could outshine the entire Milky Way for weeks when it explodes
- UY Scuti does not have a habitable zone
- UY Scuti is expected to heat up
- UY Scuti cannot fuse elements any further after iron
What is the life cycle of the UY Scuti?
UY Scuti is in the late stages of its life cycle and has entered the final stages of its life. UY Scuti is likely ending its life cycle because it is beyond the main sequence phase of stellar evolution. UY Scuti is in its later years as a red supergiant. UY Scuti is massive enough to end its life as a fiery supernova. UY Scuti is expected to simulate life cycles of stars. UY Scuti is living out its golden years as a red supergiant but has a short lifespan.
UY Scuti has a short lifespan compared to smaller stars. UY Scuti is fusing helium in its core and hydrogen around its core. UY Scuti will go through a core-collapse supernova because it has depleted the hydrogen fuel in its core. The star’s life will end in an explosion. UY Scuti is only 10-20 million years old but is living out its golden years and is on a path toward an explosive end.
UY Scuti has a pulsation period of 740 days and has used up most of its hydrogen fuel. UY Scuti will explode as a type IIb supernova or may only have a few million years left. UY Scuti might become a Wolf-Rayet star because it burns through its fuel quickly. UY Scuti might explode as a type Ib/Ic supernova or type IIn supernova. UY Scuti will eject its outer layers and might become a luminous blue variable.
UY Scuti is expected to evolve back to hotter temperatures. UY Scuti might explode in a supernova because it has begun to fuse helium instead of hydrogen. UY Scuti might leave behind a neutron star. UY Scuti may explode in a supernova and will expose the core. UY Scuti’s radius will change over time as a variable star.