Omega Nebula: Definition, Distance, Age, Facts
The Omega Nebula, catalogued as M17 and NGC 6618, is a massive H II region. The nebula is a vast interstellar cloud of dust and gas lying about 5,500 light-years from Earth. Acting as a gigantic stellar nursery, the Omega Nebula is one of the youngest and most massive star-forming regions in the Milky Way, continuously forging new stars within its huge cloud of gas.

What is the Omega Nebula?
The Omega Nebula is a vast interstellar cloud of dust and gas, which is giving birth to young, hot stars and is located by some of the richest starfields of the Milky Way. It is known as the Swan Nebula or M17, was catalogued by Charles Messier in 1764, and is located 5,500 light-years from Earth in Sagittarius.
The Omega Nebula is a massive H II region and a bright emission nebula excited by young stars. It is a giant molecular cloud located in the Sagittarius-Carina spiral arm of the Milky Way galaxy, and is one of the largest star-forming regions in our galaxy. As a stellar nursery and star factory sculpted by stellar winds and radiation, it glows as a source of radio emission in the constellation Sagittarius.
Catalogued as Messier 17 (M17) and NGC 6618, the nebula is better known under the collective nickname Omega Nebula, although it also bears at least five proper names: Checkmark Nebula, Horseshoe Nebula, Lobster Nebula, Swan Nebula, and Omega Nebula
.

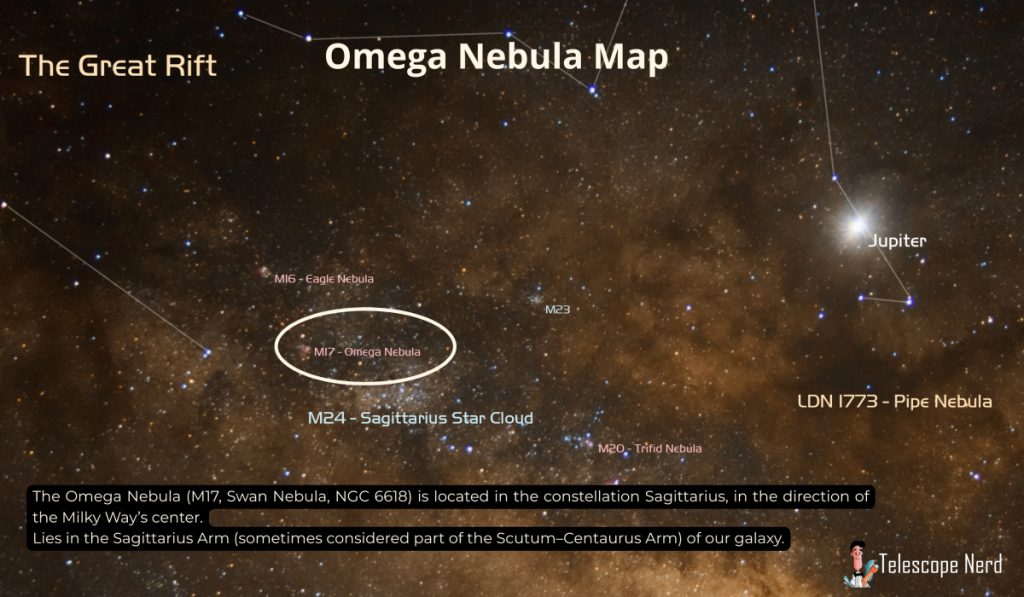
How far away is the Omega Nebula?
The Omega Nebula lies between 5,000 and 6,000 light-years from Earth, with most estimates placing it around 5,500 light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius.
How big is the Omega Nebula?
The Omega Nebula spans 15 light-years in diameter. The cloud of interstellar matter of which this nebula is a part is roughly 40 light-years in diameter. The Omega Nebula has an apparent size of 20 x 15 arc minutes. The total mass of the Omega Nebula is estimated at 800 solar masses.
What is the age of the Omega Nebula?
The Omega Nebula has an estimated age of 1 million years. This makes the young stars within M17, the Omega Nebula, roughly 1 million years old.
What is special about the Omega Nebula?
The Omega Nebula is one of the brightest nebulae in the night sky. It emits optical light, infrared radiation and radio waves. Ultraviolet radiation causes the cosmic cloud to glow. Omega Nebula is one of the largest star-making areas of space currently visible to our telescope technology. It lies at the edge of a dark gas cloud in which new stars are being born. It is richer in both star-forming material and young stars than M42.
Messier 17 contains many newly-born stars. It hosts one of the youngest star clusters in the Milky Way. The region contains nine stars of spectral type O and up to 800 stars overall. The nebula is sculpted by stellar winds and radiation.
The nebula is visible from Earth and is located in the constellation of Sagittarius. Omega Nebula is observable through a small telescope and is just on the limit of naked-eye detection in good conditions.

